
Treatment is generally deferred until at least age 8, when an adult gait pattern is typically established, and compensatory mechanisms can be evaluated. Once the bone is healed, patients can return to unrestricted activity. The fixation method depends on the patient’s age, associated differences, and other variables.

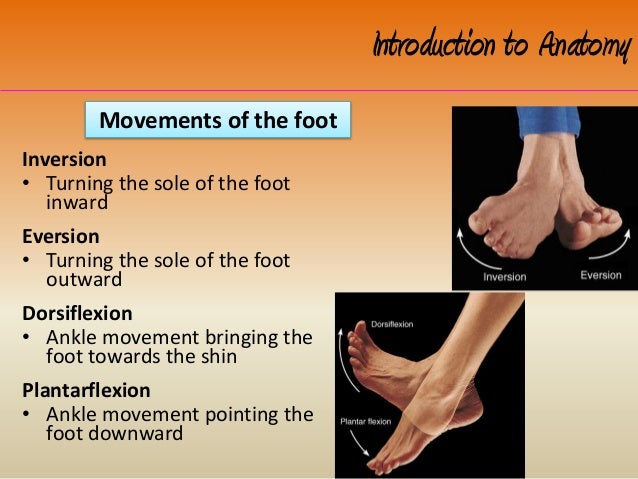
Treatment requires an osteotomy (bone cut) to realign the bone and fixation with a plate, rod, or external fixator. Unfortunately, bracing for internal tibial torsion is ineffective. Severe deformity that limits the ability to walk with a normal foot progression angle can lead to discomfort as adjacent joints struggle to accommodate the difference. Often, the difference does not lead to symptoms, and can be observed. Often, some degree of metatarsus adductus is present, which worsens the overall appearance.Treatment of metatarsus adductus in small children is generally not indicated, as braces have been shown to be ineffective. The amount of torsion in the tibia (shin bone) is recorded by having the patient lie on their stomach and then the angle between the foot and the thigh is measured. Patients may notice that when they stand and walk, the knee points forward, but the foot points in. Internal tibial torsion (when the shin bone turns inward): When the rotational difference is located in the lower leg, examination focuses on determining the level of the rotational difference, the magnitude of the difference, as well as screening for any associated differences.In some instances, surgical treatment is needed for patients with other symptoms. In older children and adults, metatarsus adductus is typically an issue of appearance. Checking for hip dysplasia is most important in firstborn female babies, especially if there is a family history of dysplasia. Infants with this foot shape should be evaluated for hip dysplasia, as it is often considered a “packaging disorder.” In plain terms, this means that the space available for the baby in the womb was small enough that the baby was packed in tightly, limiting motion and resulting in the shaping of the foot. Regular follow-up appointments are scheduled to be sure that the brace is fitting well and that the foot is responding appropriately. This process is similar to, but less involved, than treatment of clubfoot. Metatarsus adductus can be treated with special braces for the foot, which help form the foot into a more typical shape. Metatarsus adductus (when the foot turns inward): For the bean-shaped foot, examination focuses on the flexibility of the foot and screening for associated problems.In-toeing is most commonly linked to one of three factors: a bean-shaped foot (metatarsus adductus), an internal twist in the lower leg (internal tibial torsion), or an internal twist of the femur (femoral anteversion). In-toeing is when the feet turn inward instead of pointing straight ahead. Older patients with rotational deformities often present with hip or knee pain, and they only find out about the rotational difference in retrospect. The orthopedic specialist will conduct a thorough physical examination to determine the cause of the rotational deformity and will get the family and patient history to determine risk factors for other orthopedic problems. The evaluation and treatment of rotational differences depend primarily on two factors: the patient’s age and associated symptoms.
Most commonly, rotational deformities are noticed by parents of young children and brought to the attention of pediatricians who refer the patient to an orthopedic specialist. How are rotational deformities diagnosed and treated? There is often no pain associated with the rotational difference, but this is not always the case. In-toeing and out-toeing are some of the most common concerns seen in an orthopedic deformity practice. Rotational deformities occur when the foot or a leg bone are turned or twisted inward or outward, and this causes the feet to turn inward or outward rather than pointing straight ahead.

Share Tweet Email Print What are rotational deformities of the foot and leg?


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
